Why is the southern United States prone to hurricanes in December

Alyssa HaasAnd Middle Tennessee State University s Kelsey EllisAnd University of Tennessee
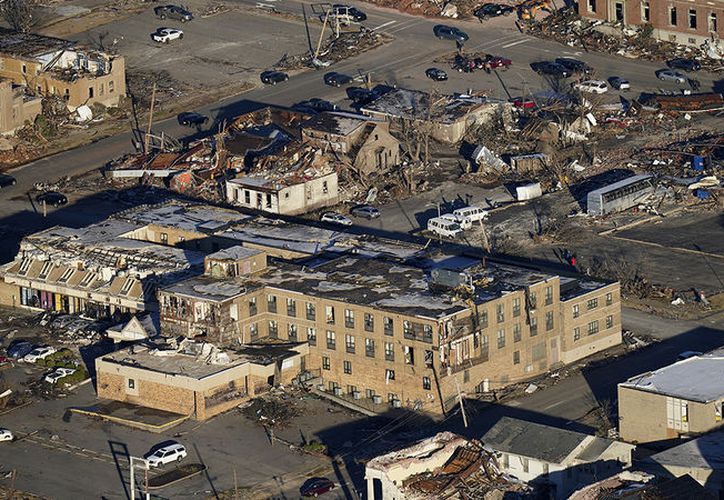
On the night of December 10-11, 2021, a wave of powerful tornadoes swept through parts of Arkansas, Mississippi, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Illinois, killing all dozens of people They left a trail of destruction for hundreds of kilometers. Climate scientists who specialize in hazards Alyssa Haas s Kelsey Ellis They explain the conditions that gave birth to this phenomenon and why the Southeast is prone to these disasters throughout the year, especially at night.
What factors combined to cause such a high rise?
On December 10, a powerful storm system approached the central United States from the west. While this system left heavy snow and rain in the cooler West and North Midwest, the South had near-record temperatures, thanks to warm, moist air blowing northward from the Gulf of Mexico.
The storm system brought dense cold air to the area, which interacted with the warm air, creating Unstable weather conditions. When warm and cold air masses collide, the less dense warm air rises toward the cooler levels of the atmosphere. As this warm air cools, the moisture it contains condenses into clouds and Storms can form.
When this instability is combined with large wind shear Winds that change direction and speed at different altitudes in the atmosphere can create an ideal formation for powerful spinning storms.
On a hurricane rating scale, how severe is it?
Reported at least 38 tornado In six states during this wave, which caused The prevalence of power outages, damage and deaths. The United States National Weather Service ranks hurricanes based on the severity of damage using 28 damage indicators from Enhanced Fujita Scale, or EF. Storm assessments and hurricane assessments can take several days or longer to complete.
As of December 12, it has been confirmed at least four EF-3 and five EF-2 Hurricanes. The EF-2 and EF-3 tornadoes are powerful, with wind speeds of 179-218 km / h and 219-266 km / h, respectively.
Strong straight-line winds also occur with severe storms and can cause as much damage as a hurricane. After recordings of storms and tornadoes, the National Weather Service conducts damage studies in person to determine whether a hurricane or winds caused the reported damage and the degree of destruction. Researchers will look to see if debris is scattered in only one direction, which may indicate straight line winds, or in different directions, which characterizes a tornado.
Hurricane traveled 386 km through four states. Why is it unusual?
Most hurricanes stay on Earth for a short time and They travel short distances, From 5-6 kilometers on average. Hurricanes with a long, very long path – those hurricanes that travel 40 and 170 kilometers respectively– Relatively rare. Concentration less than 1% For all hurricanes in the United States.
Long-term hurricanes require A very specific set of ingredients which should be located in a wide area. These rare tornadoes are formed from one super storm – A storm with a rotating updraft called misocyclone– which can last for hours.
More significant hurricanes tend to stay on the ground longer than weaker hurricanes. their tracks For a long time, especially in the southeast, where the major cyclones in the cold season move quickly, thus covering more land.
the previous record The tornado was a long-distance tornado in 1925, when an F-5 Tri-State tornado traveled 352.45 kilometers through Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana. Recently, a “four-nation hurricane”, as it was called, is expected to occur Breaking this record!. In the coming days, the US National Weather Service will confirm whether the hurricane has been on the ground for more than 200 miles or if multiple tornadoes have occurred from the same storm. Agency issued a Initial rating of EF-3 or higher for this phenomenon.
Why do more winter and nighttime hurricanes occur in the southeastern United States?
Spring is usually considered hurricane season, but hurricanes can strike at any time of the year. Southeast experiences of the United States a second peak Hurricane activity is in the fall and early winter, and winter cyclones are common.
Also, tornadoes can strike at any time of the day. that night especially common In the southeast, where components for storms Different and more suitable for nocturnal hurricanes than in “Hurricane Alley” (“Tornado Alley”) in the Great Plains.
Tornado storms in the Southeast are usually driven by high wind shear. They do not depend much on the rise of warm and moist air that produces atmospheric instabilityThese conditions require a diurnal warming of the Earth’s surface, and their frequency increases in the spring.
This phenomenon was expected need to I predicted a significant increase several days ago. the Storm Forecasting Center The National Weather Service in Norman, Oklahoma, and the affected National Weather Service local forecast offices have issued timely warnings, warnings and information about staying safe.
But hurricanes can be night especially deadly. Mortality tends more because people often Do not receive warning messages when he is asleep. Storm detection Harder in the dark, people More likely to be in more vulnerable homes, such as mobile homes, at night compared to the day, when they are working in sturdier buildings.
get rid of Different and reliable ways to receive alerts at night This is essential, as the power supply and mobile phone service can be down during bad weather. Unfortunately, during the phenomenon of December 10 and 11, some people who went to the shelters died When tornadoes hit the building Where were they? But timely warnings that allow people to take refuge safely in a sturdy and robust structure can mean surviving during less devastating events.![]()
Alyssa Haasassistant professor of geography, Middle Tennessee State University s Kelsey EllisAssociate Professor of Geography, University of Tennessee
This article was originally published Conversation. Read the A native.
You may also be interested in:
Winter and the common cold: everything you need to know to combat them
What is the difference between vaccine doses for children, adolescents and adults?
Study: How much sleep do you need to avoid feeling tired?

“Coffee fanatic. Gamer. Award-winning zombie lover. Student. Hardcore internet advocate. Twitter guru. Subtly charming bacon nerd. Thinker.”