Can “slow earthquakes” help predict large earthquakes?

Being able to predict when a major earthquake will occur is a yearning that seismologists share.
It is impossible with current knowledge and technology, but research in recent years has led to expertsto be One step To determine When the conditions are met On the ground for a great earthquake.
Geophysicists have focused, among other fields, on the so-called ‘Slow earthquakes’.
It is about “landslides that happen.” In a geological errorIn general and in particular In theSubduction zones Between two connected plates, “seismologist Victor Cruz-Atienza, a researcher at the Institute of Geophysics of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, explains to BBC Mundo.
The expert and his colleagues recently published a study of these types of earthquakes that develop in certain seismic zones, such as those in southeastern Mexico, where there are two interacting plates.
His research determined that There were slow earthquakes, Also called silent, At the back of the last four Earthquakes Larger size In that country.
Unlike surface tremors, Slow earthquakes release energy bit by bitOver the course of weeks or monthsMaking it imperceptible and not destructive at all.
But experts say Study it It is very important To better understand how earthquakes are created, since then Not always slow someone expects a “normal”But it is a factor to take into consideration.
Read also: UNESCO awards CDMX for its resilience in the face of earthquakes and the Covid-19 pandemic
Professor Sergio Ruiz, of the Department of Geophysics at the University of Chile, told BBC Mondo: “Observing slow earthquakes in the past 20 years opens a window for us to understand the physics that govern earthquakes.”
It will also open Earthquake Prediction Window. But at the present time it is necessary to enter and build the model, so why does this happen sometimes and not in all cases. “
What happens in the rear
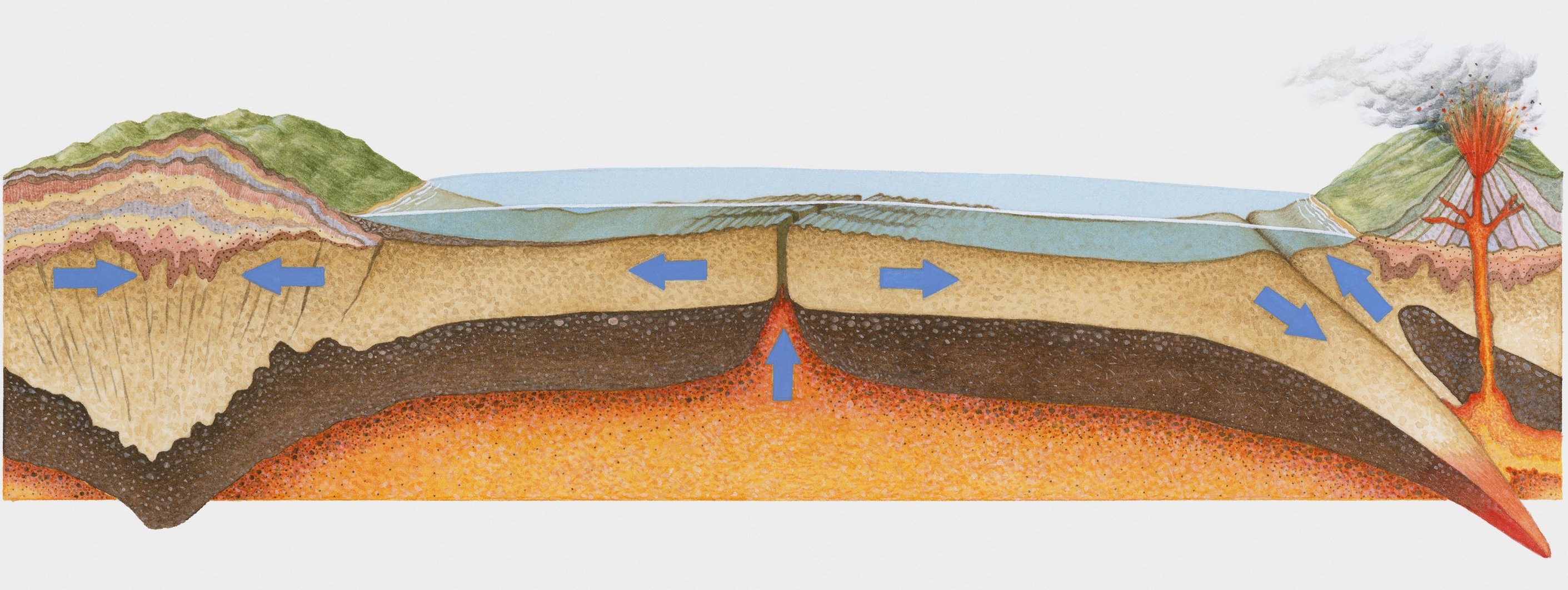
Earthquakes generally occur When plate tectonics, surface energy is released, Causing the ground to vibrate sharply.
In this video you can see it graphically.
However, there are other types of interactions in lower or higher layers of earthquakes that are felt at Earth’s surface.
One such event is slow earthquakes that cannot be observed because they do not release energy suddenly.
Ruiz points outSome It reached size 7 On the Richter scale, Which would be a great risk if earthquakes with consequences on the surface, but the fact that they occur over a period of weeks or months eliminates the danger.
It’s as if there were plates, cups and cutlery on a table, the Chilean geophysicist explains. If that table was moved quickly, what was on top would vibrate. But if the government moves too slowly, things will practically remain the same.
“A slow earthquake can be about the same magnitude as a large earthquake, like a” normal “earthquake,” says Ruiz, “but because it is moving very slowly, it is not perceptible.”
Cruz Atienza explains that it can be measured With tools from Differential GPS, “very high accuracy”, Which measures the deformation of the continents with an accuracy of nearly 2 millimeters.
The expert says: “Through this, we can measure the extent of the deformation of the continent and how there is an elastic recovery, and the return of the slow slide or slow earthquake, with contact with the plates under the continent.”
Behind the great earthquakes
By studying slow earthquakes, scientists determined that many of the large earthquakes that rocked different regions of the world were as well Directed by These “silent” events.
Among them was the earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 in 2011 in JapanCausing a tsunami and the failure of the nuclear power plant Fukushima. Also 7.8 degrees in New Zealand in 2016 Or the from Chile from 2014 8 degrees2.
In the case of Mexico, Cruz Atienza determined that slow earthquakes preceded four major earthquakes in the country, including those in September 2017 that caused buildings to collapse in Mexico City, as well as the earthquake that occurred in February 2018 near Pinotiba. Nacional.
“We have shown the stresses or distortions that this slow and deep earthquake created in the most shallow area of plate contact, and that it caused the rupture of this 7.2-magnitude earthquake that caused severe damage in Pinotiba,” the expert explains. .
His research in southern Mexico found slow earthquakes Every 3.5 years in Guerrero’s state All 1,5 Years In Oaxaca, A product of the slipping of the Cocos Plate (oceanic) and North America (continental).
Every region of the world has its own frequency.
However, both Cruz Atienza and Royce caution that with current evidence, It cannot be said that slow earthquakes are a permanent phenomenonN a Produce Earthquakes on the surface.

“There are many slow earthquakes that did not produce earthquakes. Slow earthquakes, at least with the monitoring capacity we have today, appear to be a necessary but not sufficient condition to induce an earthquake. There must be other conditions to produce them,” he explains. Cruz Atienza.
What do scientists know then?
The study of slow earthquakes is an important advance for researchers to obtain evidence that activity in the Earth’s crust is advancing toward an event with devastating potential.
“They have allowed the scientific community Much better understanding of the behavior of geological faults Where dangerous earthquakes occur. The Mexican researcher says that these slow earthquakes, which we do not realize, modify the state of pressures, tensions and distortions in the continental crust that could ultimately cause large earthquakes.

Observing slow earthquakes has only occurred in the past 20 years, but for Ruiz “opens a window to understanding the physics that govern earthquakes.”
“It remains very difficult to conclude whether slow earthquakes are a general observation. Since there are not many recorded slow earthquakes, the question remains. These observations must be tried in order to Continuing to maintain it over time to be able to make more accurate conclusionsRuiz says.
Read also: 90% of earthquake-damaged buildings will be restored in 2022
What does science need to predict the possibility of a dangerous earthquake?
The researchers agree that it requires More monitoring and research On how to create these events.
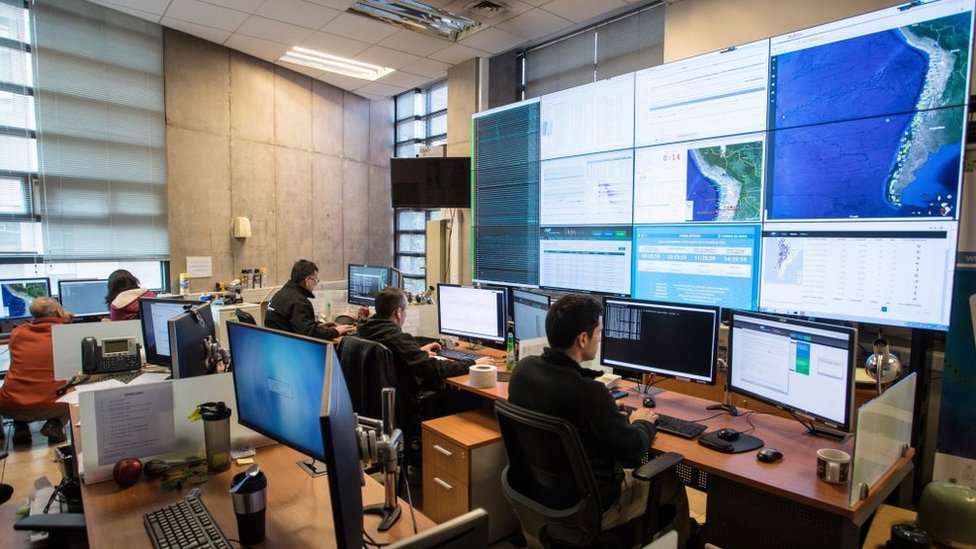

In addition, it is necessary The Installation More Measurement tools Along seismic zones, such as those over the entire Pacific coast of Latin America.
“Right now, what we lack most is augmentation of devices to be able to measure earthquakes in a ground-based way. To get a lot of data and if everything corresponds to being preceded by a slow earthquake,” Ruiz explains.
And although there are many geophysical investigations in Latin America, the region still lags behind in the field of instrumentation compared to other parts of the world.
You can now receive notifications from BBC News Mondo. Download and activate our app so that you don’t miss out on our best content.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=96ijHXnxBw8

“Award-winning zombie scholar. Music practitioner. Food expert. Troublemaker.”


/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/AHVYMMDSTZDTDBFNZ3LMFUOKNE.jpg)