Scientists create a complete human family tree
Posted:
February 25 2022 16:23 GMT
The reconstruction includes up to two million years of human evolution.
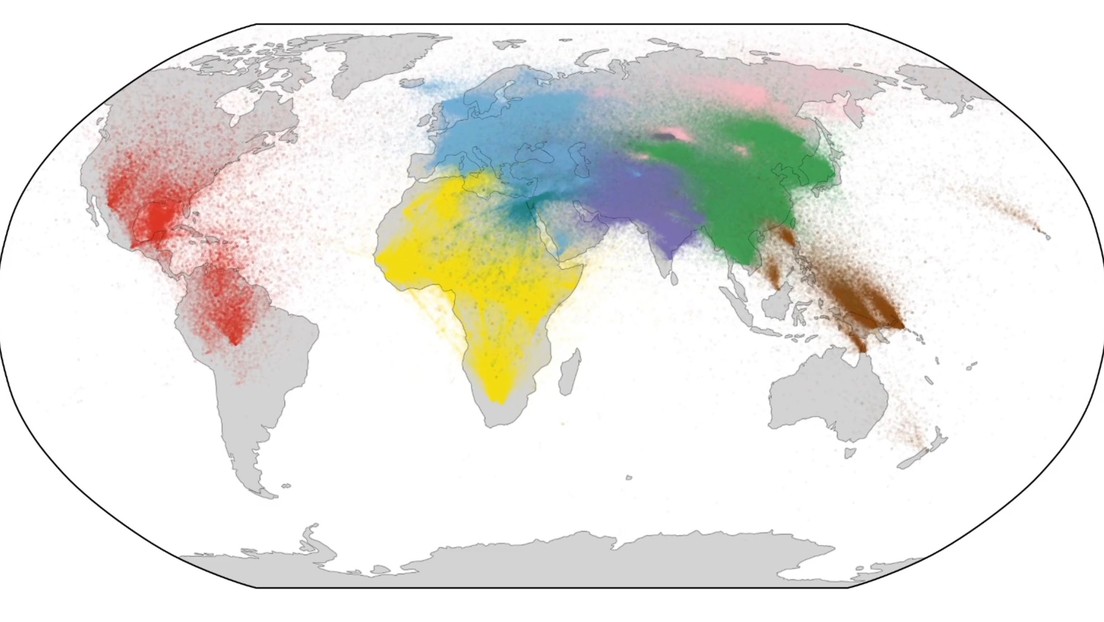
Researchers from the UK’s Big Data Institute have mapped humanity’s most comprehensive family tree to date, spanning as much as two million years to the present, since the ancestors of modern humans were still tree-climbing in northeastern Africa.
The team measures the human past not so much in years, but in generations, and diagnoses tens of thousands of them in their ancestral lineages. He seeks to trace the origin of each, whose genome has at some point been included in one of the available databases. The studypublished in Science on February 25, divided the modern human genome into groups, according to kinship kinship, and reconstructed how all current genetic variations are created.
Since individual genomic regions are inherited only from either the father or the mother, the origin of each stretch of the genome can be represented as a tree, as the researchers explain in release. This group of trees connects genetic regions through time with ancestors and with Put it on the map where it first appeared All genetic variation.
This approach makes it possible to visualize when and where these ancestors lived “with very few assumptions about the underlying data”. The modern sample consists of 3609 single genome sequencedof 215 groups, while the ancient genome is few and includes three Neanderthal genomes, one Denisovans and a family of four who lived in Siberia about 4,600 years ago.
The algorithms used predicted where common ancestors should be in phylogenetic trees to explain patterns of genetic variation. The resulting network included, among the thousands of genetic codes in the input, nearly 27 million ancestors, and the lost relationships between individuals and populations were retrieved by machine.
“Essentially, we created a large family tree, Genealogy of all mankind One of the study’s lead authors, evolutionary geneticist Yan Wong, said, “These models as accurately as possible the history that generated every variation in the modern human genome.
In addition, the team considered the algorithm used as a “robust platform for compiling genetic data and investigating human history and evolution,” but also for other species: from uncivilized human beings Even bacteria.

“Evil coffee nerd. Analyst. Incurable bacon practitioner. Total twitter fan. Typical food aficionado.”

:quality(70):focal(288x128:298x138)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/metroworldnews/4VWFN4IMGFGQTCCSYSVPIJDM4A.jpg)









